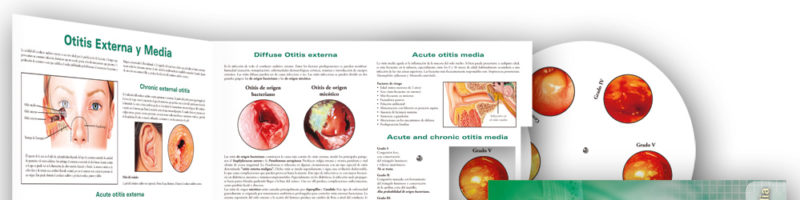
1) The production of cerumen or wax which, while preserving the normal flora, it acidifies the area and is capable of destroying the bacteria and fungi that are pathogenic for the body.
2) The epithelium of the canal has cells that specialize in continuously sweeping all elements that are alien to the ear, from the membrane to the auricle.
When one of these two systems is impaired, infection of the external auditory canal results.
1) Se produce el cerumen o cera que acidifica el medio y tiene la propiedad de destruir las bacterias y hongos que son patógenos para el organismo, conservando la flora normal.
2) El epitelio del canal tiene células especializadas en barrer continuamente todos los elementos extraños al oído desde la membrana hacia el pabellón auricular.
Cuando alguno de estos dos sistemas se ve interrumpido se produce la infección del conducto auditivo externo.